AbstractEditor is the base class for edit screen controller. It is a subclass of AbstractWindow.
When creating a controller class, it is recommended to parameterize AbstractEditor with the edited entity class. This enables getItem() and initItem() methods work with the specified entity type and application code does not need to do additional type conversion. For example:
public class CustomerEdit extends AbstractEditor<Customer> {
@Override
protected void initItem(Customer item) {
...
AbstractEditor defines the following own methods:
-
getItem()– returns an instance of the entity being edited, which is set in the main data source of the screen (i.e. specified in thedatasourceattribute of the root element of the XML-descriptor).If the instance being edited is not a new one, screen opening procedure will reload the instance from the database with the required view as set for the main data source.
Changes made to the instance returned by
getItem(), are reflected in the state of the data source and will be sent to the Middleware at commit.It should be considered that
getItem()returns a value only after screen is initialized withsetItem()method. Until this moment, this method returnsnull, for instance when calling from insideinit()orinitItem().However, in the
init()method, an instance of an entity passed toopenEditor()can be retrieved from parameters using the following approach:@Override public void init(Map<String, Object> params) { Customer item = WindowParams.ITEM.getEntity(params); // do something }initItem()method requires an instance to be passed explicitly and of an appropriate type.In both cases the obtained entity instance will be reloaded afterwards unless it is a new one. Therefore you should not change it or save it in a field for future use.
-
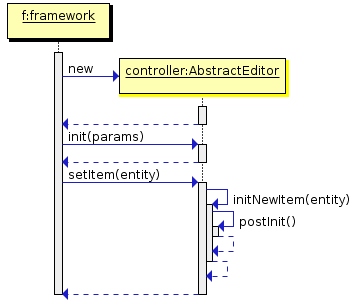
setItem()– invoked by the framework when a window is opened usingopenEditor()to set the instance being edited to the main data source. By the moment of invocation all screen components and datasources will have been created and the controller’sinit()method will have been executed.It is recommended to use template methods
initNewItem()andpostInit(), instead of overridingsetItem()in order to initialize a screen. -
initNewItem()– a template method invoked by the framework before setting the edited entity instance into the main data source.The
initNewItem()method is called for newly created entity instances only. The method is not called for detached instances. This method can be implemented in the controller, if new entity instances must be initialized before setting them in the data source. For example:@Inject private UserSession userSession; @Override protected void initNewItem(Complaint item) { item.setOpenedBy(userSession.getUser()); item.setStatus(ComplaintStatus.OPENED); }A more complex example of using the
initNewItem()method can be found in development recipes section. -
postInit()– a template method invoked by the framework immediately after the edited entity instance is set to the main data source. In this method,getItem()can be called to return a new entity instance or an instance re-loaded during screen initialization.This method can be implemented in controller for final screen initialization, for example:
@Inject protected EntityDiffViewer diffFrame; @Override protected void postInit() { if (!PersistenceHelper.isNew(getItem())) { diffFrame.loadVersions(getItem()); } } -
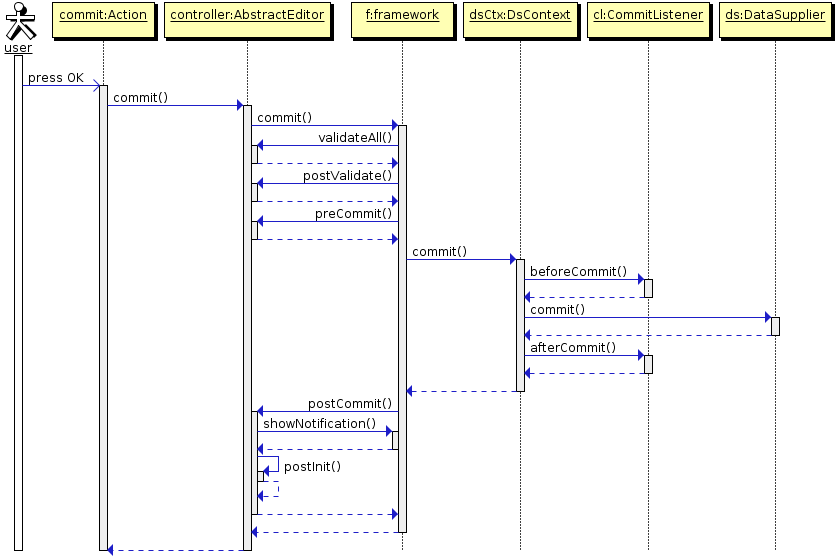
commit()– validates the screen and submits changes to the Middleware via DataSupplier.If a method is used with
validate = false, commit does not perform a validation.It is recommended to use specialized template methods –
postValidate(),preCommit()andpostCommit()instead of overriding this method. -
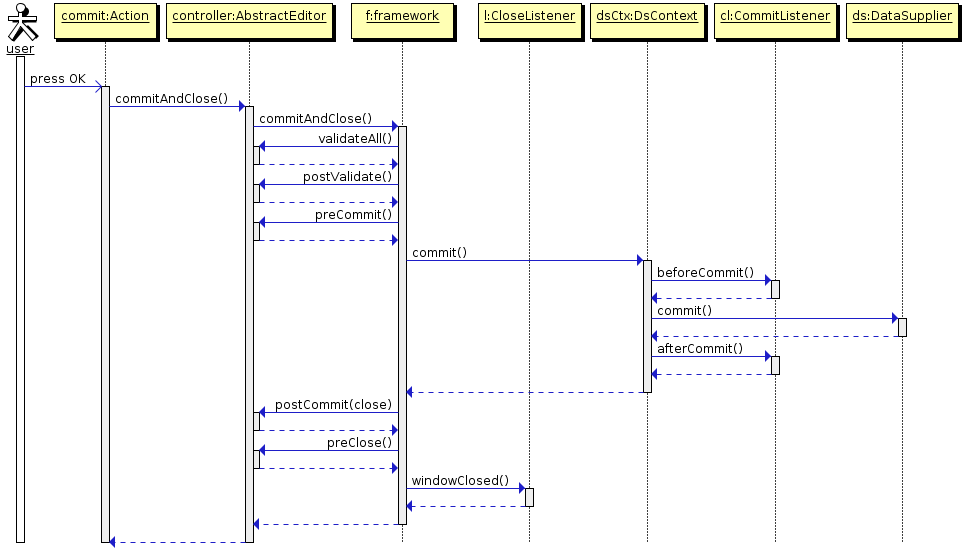
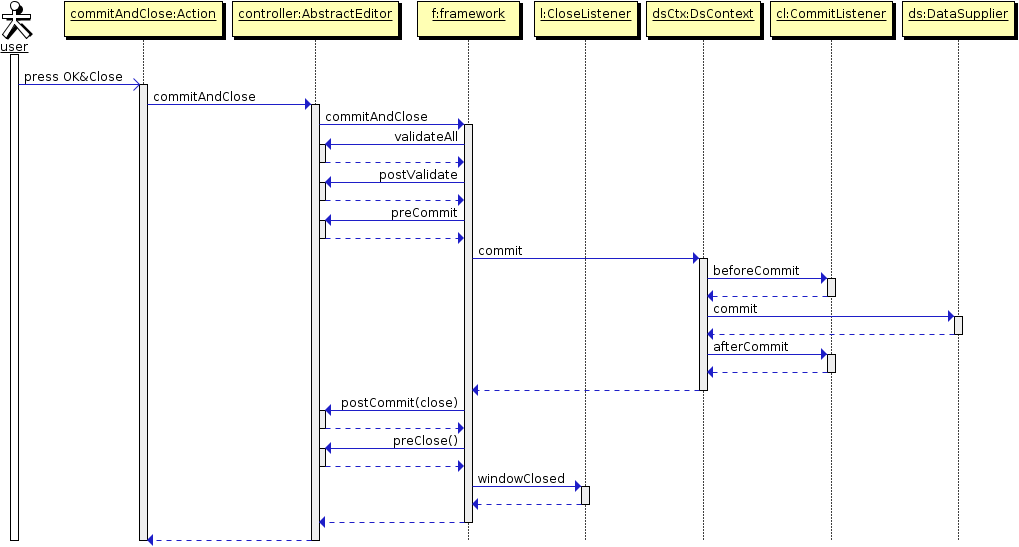
commitAndClose()– validates the screen, submits changes to the Middleware and closes the screen. The value of theWindow.COMMIT_ACTION_IDwill be passed to thepreClose()method and registeredCloseListenerlisteners.It is recommended to use specialized template methods –
postValidate(),preCommit()andpostCommit()instead of overriding this method. -
preCommit()– a template method invoked by the framework during the commit process, after a successful validation, but before the data is submitted to the Middleware.This method can be implemented in controller. If the method returns
false, commit process gets interrupted, as well as window closing process (ifcommitAndClose()was invoked). For example:@Override protected boolean preCommit() { if (somethingWentWrong) { showNotification("Something went wrong", NotificationType.WARNING); return false; } return true; } -
postCommit()– a template method invoked by the framework at the final stage of committing changes. Method parameters are:-
committed– set totrue, if the screen had changes and they have been submitted to Middleware. -
close– set totrue, if the screen should be closed after the changes are committed.
If the screen does not close the default implementation of this method displays a message about successful commit and invokes
postInit().This method can be overridden in controller in order to perform additional actions after successful commit, for example:
@Inject private Datasource<Driver> driverDs; @Inject private EntitySnapshotService entitySnapshotService; @Override protected boolean postCommit(boolean committed, boolean close) { if (committed) { entitySnapshotService.createSnapshot(driverDs.getItem(), driverDs.getView()); } return super.postCommit(committed, close); } -
The diagrams below show initialization sequence and different ways to commit changes for an edit screen.