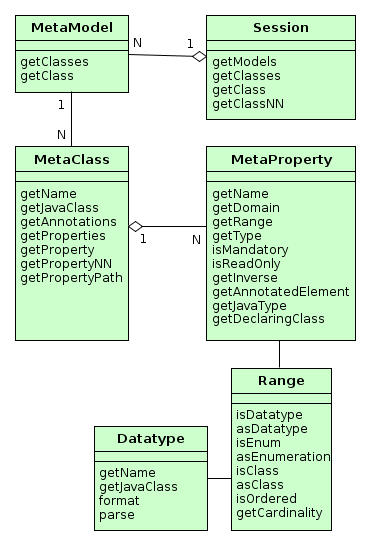
Let us consider the basic metadata interfaces.
-
Session -
Entry point of the metadata framework. Allows obtaining
MetaClassinstances by name and by the corresponding Java class. Note the difference in methods:getClass()methods can returnnullwhilegetClassNN()(NonNull) methods cannot.Sessionobject can be obtained usingMetadatainfrastructure interface.Example:
@Inject protected Metadata metadata; ... Session session = metadata.getSession(); MetaClass metaClass1 = session.getClassNN("sec$User"); MetaClass metaClass2 = session.getClassNN(User.class); assert metaClass1 == metaClass2; -
MetaModel -
Rarely used interface intended to group meta-classes.
Meta-classes are grouped by the root name of Java project package specified in metadata.xml file.
-
MetaClass -
Entity class metadata interface.
MetaClassis always associated with Java class which it represents.Basic methods:
-
getName()– entity name, according to convention the first part of the name before$sign is namespace code, for example,sales$Customer. -
getProperties()– the list of meta-properties (MetaProperty). -
getProperty(),getPropertyNN()– methods return meta-properties by name. In case when there is no attribute with provided name, the first method returnsnull, and the second throws an exception.Example:
MetaClass userClass = session.getClassNN(User.class); MetaProperty groupProperty = userClass.getPropertyNN("group"); -
getPropertyPath()– allows you to navigate by references. This method accepts string parameter – path in the format of dot-separated attribute names. The returnedMetaPropertyPathobject allows accessing the required (the last in the path) attribute by invokinggetMetaProperty()method.Example:
MetaClass userClass = session.getClassNN(User.class); MetaProperty groupNameProp = userClass.getPropertyPath("group.name").getMetaProperty(); assert groupNameProp.getDomain().getName().equals("sec$Group"); -
getJavaClass()– entity class, corresponding to thisMetaClass. -
getAnnotations()– collection of meta-annotations.
-
-
MetaProperty -
Entity attribute metadata interface.
Basic methods:
-
getName()– property name, corresponds to entity attribute name. -
getDomain()– meta-class, owning this property. -
getType()- the property type:-
simple type:
DATATYPE -
enumeration:
ENUM -
reference type of two kinds:
-
ASSOCIATION− simple reference to another entity. For example, Order-Customer relationship is an association. -
COMPOSITION− reference to the entity, having no consistent value without the owning entity.COMPOSITIONis considered to be a “closer” relationship thanASSOCIATION. For example, the relationship between Order and its Items is aCOMPOSITION, as the Item cannot exist without the Order to which it belongs.
The type of
ASSOCIATIONorCOMPOSITIONreference attributes affects entity edit mode: in the first case the related entity is persisted to the database independently, in the second case – only together with the owning entity. See Section 5.8.3, “Editing Composite Entities” for details. -
-
-
getRange()–Rangeinterface providing detailed description of the attribute type. -
isMandatory()– indicates a mandatory attribute. For instance, it is used by visual components to signal a user that value is mandatory. -
isReadOnly()– indicates a read-only attribute. -
getInverse()– for reference-type attribute, returns the meta-property from the other side of the association, if such exists. -
getAnnotatedElement()– field (java.lang.reflect.Field) or method (java.lang.reflect.Method), corresponding to the entity attribute. -
getJavaType()– Java class of the entity attribute. It can either be the type of corresponding field or the type of the value returned by corresponding method. -
getDeclaringClass()– Java class containing this attribute.
-
-
Range -
Interface describing entity attribute type in detail.
Basic methods:
-
isDatatype()– returnstruefor simple type attribute. -
asDatatype()– returns Datatype for simple type attribute. -
isEnum()– returnstruefor enumeration type attribute. -
asEnumeration()– returns Enumeration for enumeration type attribute. -
isClass()– returnstruefor reference attribute ofASSOCIATIONorCOMPOSITIONtype. -
asClass()– returns metaclass of associated entity for a reference attribute. -
isOrdered()– returnstrueif the attribute is represented by an ordered collection (for exampleList). -
getCardinality()– relation kind of the reference attribute:ONE_TO_ONE,MANY_TO_ONE,ONE_TO_MANY,MANY_TO_MANY.
-